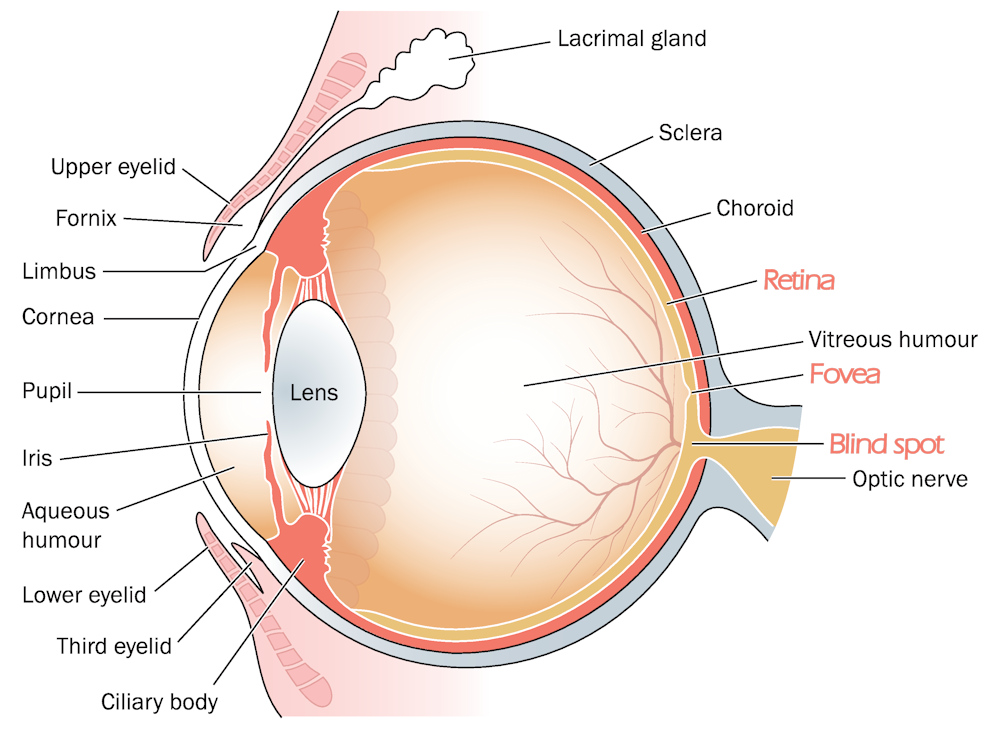
The human eye (animation)
Watch the animation above. Don't forget to click on 'discover more' (at the right) to see all animations.
- How can we see colours?
- What do you see when it's almost totally dark? Do you see colours? Do you see shapes?
- How are you able to focus on different things and see them in focus (not blurred)? Which parts of the eye are responsible for this?
- Why is something upside down projected on your retina?
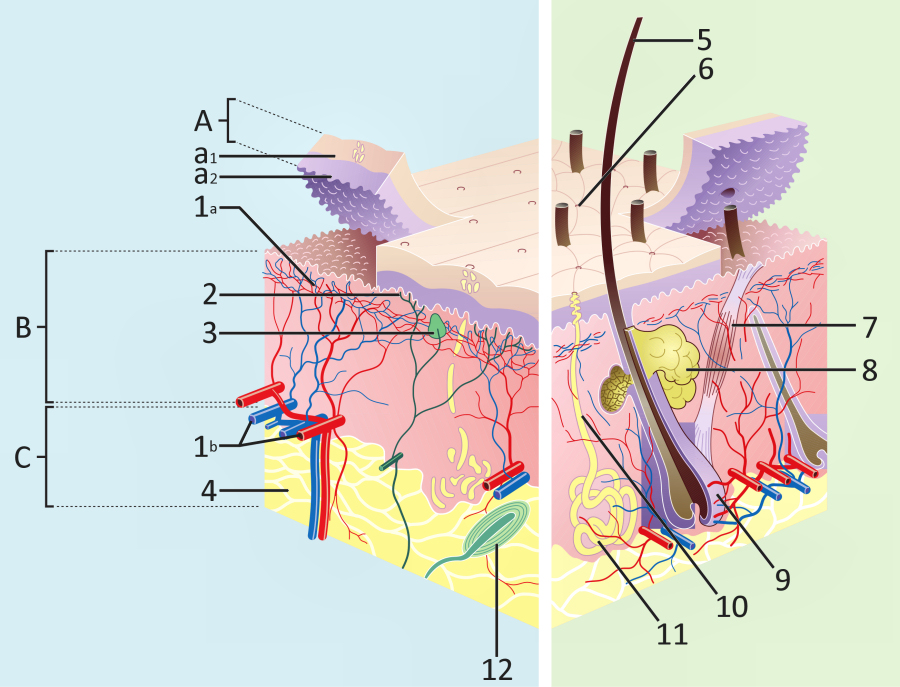
The skin
|
A. Epidermis
The outermost layer, a waterproof barrier and contains the pigments of our skin tone. B. Dermis Contains connective tissue, sweat glands and hair follicles. C. Hypodermis or subcutaneous layer Contains fat and connective tissue. |
|